Imagine a classroom where all physical resources have been digitally cataloged, all the sensors and devices have been connected to the Internet of Things and the digital map of the classroom has been merged with the object map. So, when the teacher carries her laptop to class, the lights come on automatically, the teacher's chair recognizes her and moves to accommodate her. The Interactive board switches on to her last lesson. The class mike becomes operational. The students entering class after attending a sports class having a digital wristwatch comfortably move to their seating area with any obstacle on their way like bag automatically moving away and the air conditioners adjust its cooling to suit the students present body temperature. Further, any student falling or having a mishap in the classroom, an alarm is sounded and the school nurse automatically arrives for support.
Well, is this for real? Yes, this is 'SPATIAL COMPUTING" and is the next step in the convergence of physical and digital worlds. In the Top 10 emerging technologies of 2020 shared by the World Economic Forum [https://www.weforum.org/reports/top-10-emerging-technologies-2020 ], spatial computing has a major role to play in Industry redefining itself.
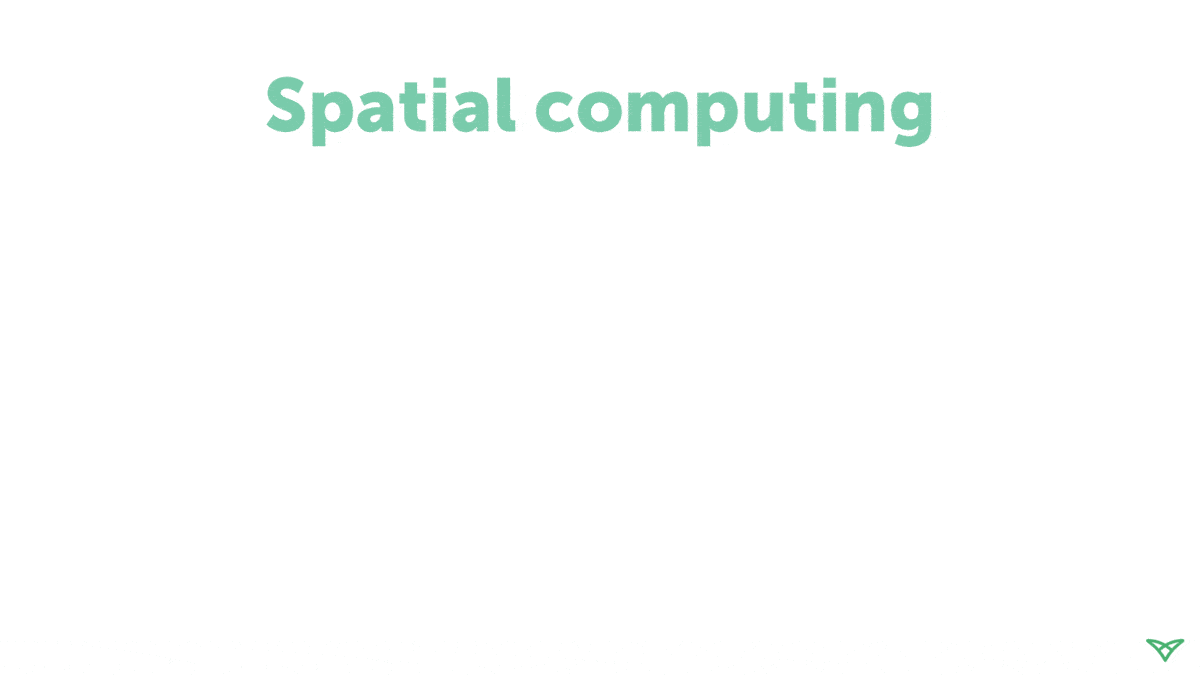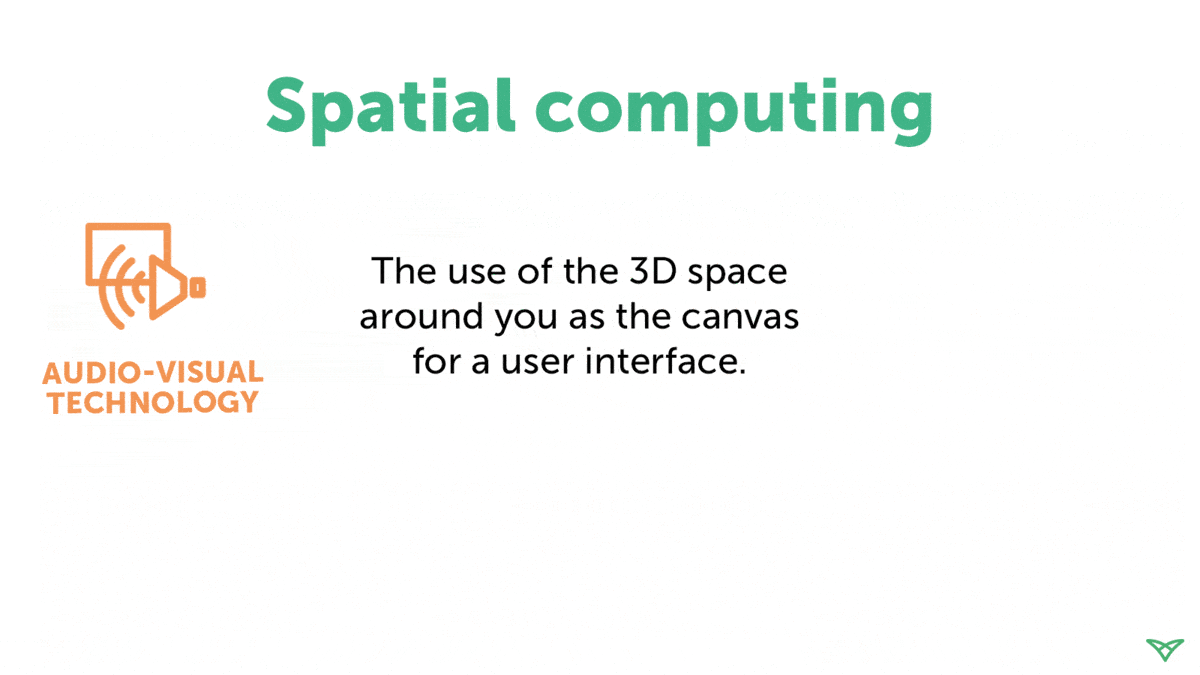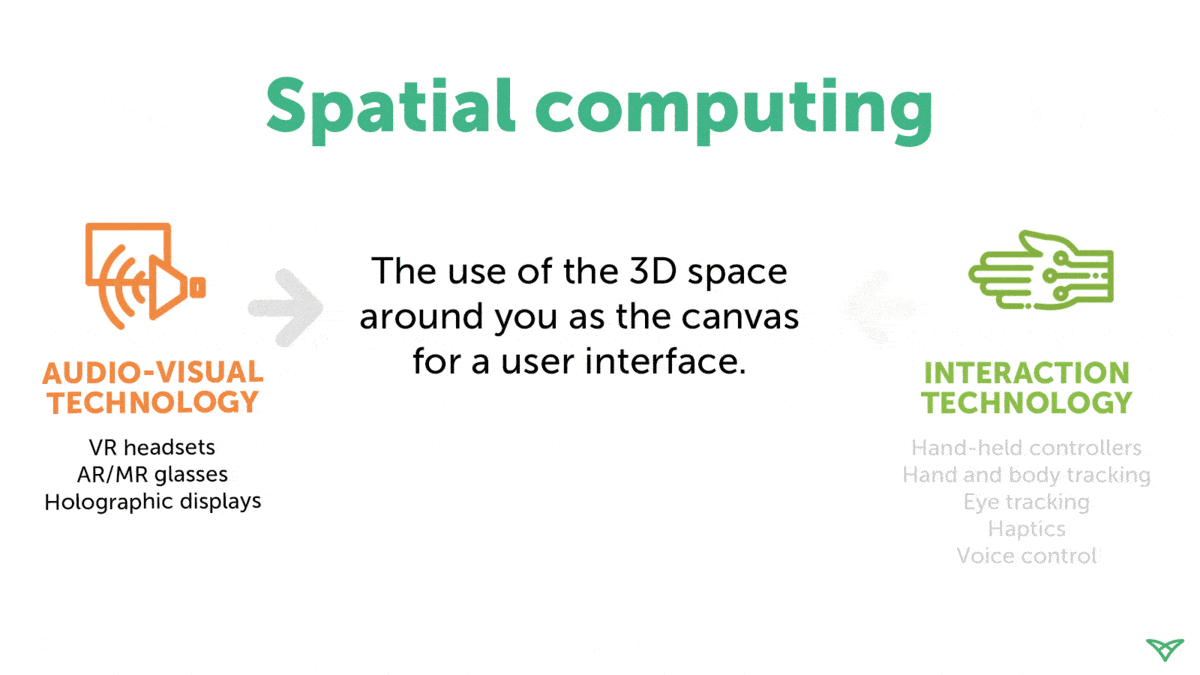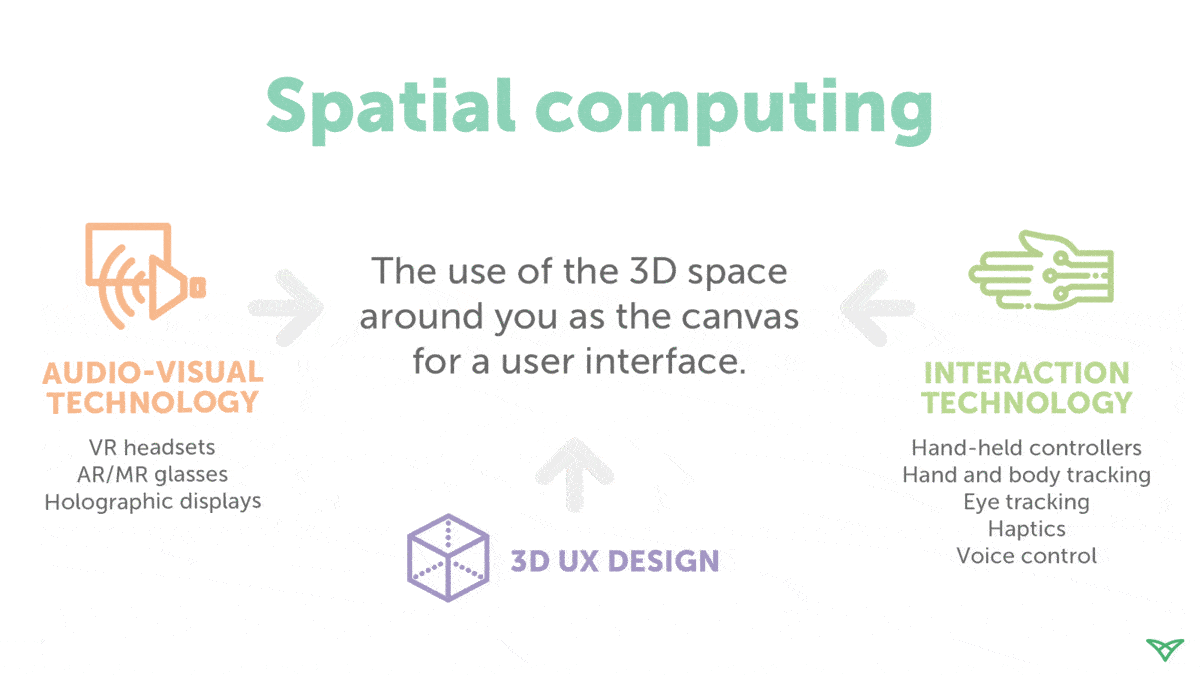
Let's understand the term spatial computing. As per Techslang, Spatial computing refers to the process of using digital technology to make computers interact seamlessly in a three-dimensional world using augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR). Spatial computing uses physical space to send input and receive output from a computer.
The video from DELL EMC WORLD CUSTOMER STORY. NIKE: VISION FOR THE FUTURE OF DESIGN makes the understanding very clear.
So let's understand this through the world of education. For starters, it enables all school processes to become streamlined, efficient, and time-saving thereby improving the quality of work.
In the case of learning, it offers experiential, interactive, and engaging learning interaction between students and teachers.
Let us study through an example: The students are studying Egyptian civilization and wish to see a collection of artifacts, mummies, coffins, stones, ancient belongings, and even food types that used to be buried with the kings before death to use in the afterlife. We connect with the Egyptian Museum in Cairo as they have connected all their artifacts to spatial computing.
The app allows multiple students and teachers to view a 3D model of a historical object from anywhere in the world and in real-time when they are using an XR [Extended Reality] headset which shifts effectively between VR and AR – ideally encompassing MR [Mixed Reality] as well. So, they created a single 3D rendering of the artifact in photorealistic form. This true-to-life replica could then be exhibited in a joint-viewing area and examined remotely by anyone, from anywhere.
The museum curator can present the digital twin of the artifact to multiple students at one time. Students seated at home can highlight, enlarge objects, examine the artifact, ask questions to the curator and also ask peer-to-peer questions. They can even walk around the artifact.
Take another case of students conducting experiments, mixing Hydrogen and Sulphur, and seeing the production of hydrogen sulphide and being able to smell the rotten eggs odour. It allows students to experiment with the materials, measurements and note down observations and arrive at conclusions based on evidence. Similarly studying a heart in 3D. Now, would one really need a laboratory?
Education then has taken up a complete transformation and physical spaces have merged with the digital making learning truly immersive. Much obviously, the teacher training will be upmost on the list ensuring that every teacher has adapted themselves to the technology and given the recent COVID 19 scenario and the manner the teachers rose to the occasion, that will be the least concern.
Further, curriculum developers, textbooks, research book publications, software companies will have to gear up to provide the students with the spatial experience. With all the recent advances, the future does seem optimistic with the world compressed by a single click.
References:
What is spatial computing: https://www.fieldbit.net/what-is-spatial-computing/
Spatial Computing in Less than 140 Characters (and more) In Gear & Tech - https://www.stambol.com/about/
What is spatial computing: https://www.ultraleap.com/company/news/blog/what-is-spatial-computing/
Transforming education and training with spatial computing: https://www.magicleap.com/en-us/news/news/transforming-education-and-training-with-spatial-computing
Vision Comic Book : https://spatialtoolbox.vuforia.com/SpatialComputing.pdf
Introduction to XR: https://www.coursera.org/lecture/xr-introduction/spatial-computing-6cz3a?utm_source=link&utm_medium=page_share&utm_content=vlp&utm_campaign=top_button
https://www.google.com/url?sa=i&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.magicleap.com%2Fnews%2Fop-ed%2Fspatial-computing-an-overview-for-our-techie-friends&psig=AOvVaw0Ep_EpfFds4UpsahQxk1wm&ust=1607754058553000&source=images&cd=vfe&ved=0CAIQjRxqFwoTCLCCyeKkxe0CFQAAAAAdAAAAABBL